Abstract
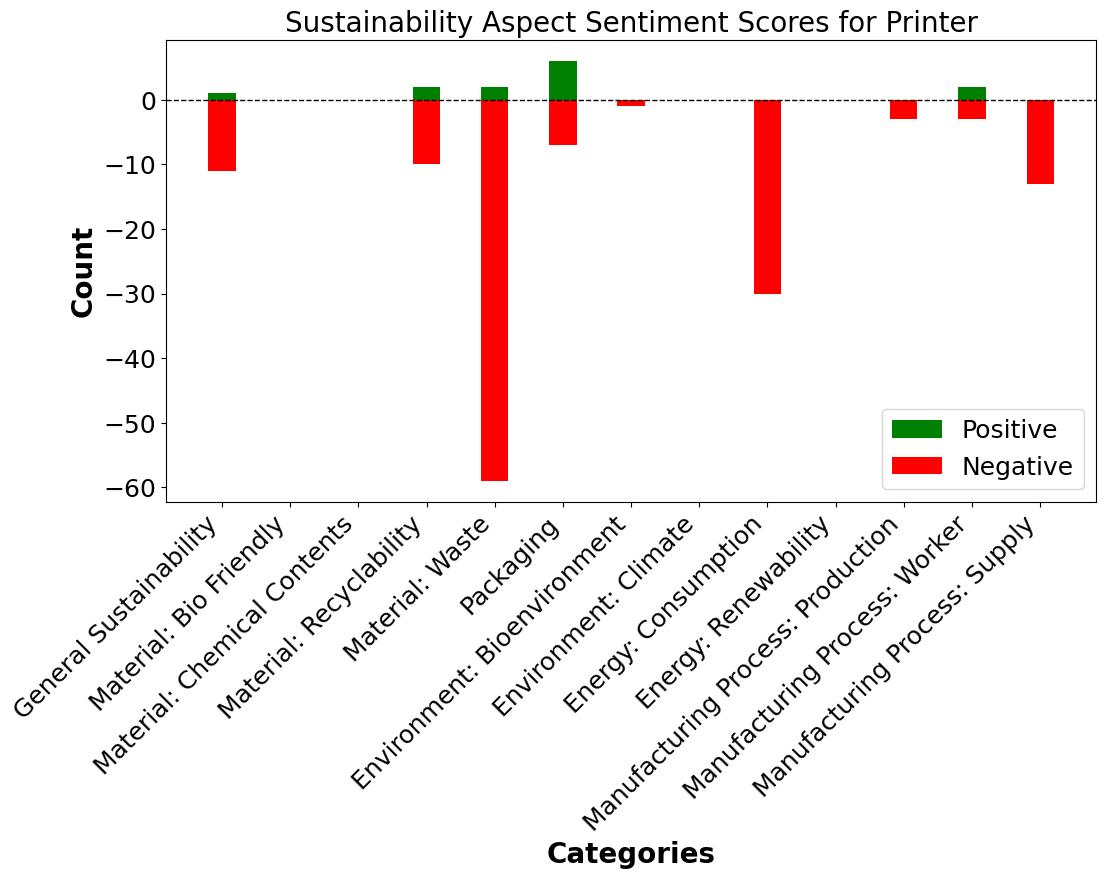
Qualitative data from user interactions with products provide a rich source of sustainability insights, revealing how users perceive and interact with sustainable product features. However, users often describe sustainability in terms of personal experiences rather than technical environmental terminology, making it challenging to extract structured insights. As a result, analyzing this feedback to inform future product design is valuable but often labor-intensive. This research explores how data-driven techniques can automate and enhance the generation of sustainable product design insights from user feedback. We constructed a database of over 23,000 Amazon customer reviews for 290 consumer products and analyzed it using aspect-based sentiment analysis (ABSA), topic modeling, and large language models (LLMs). Combining traditional NLP methods with generative models, we identified sustainability-related product concerns and valued features. A case study highlights how this approach generates product-level insights, synthesizing sustainable design leads comparable to manually-derived ones for a printer, laptop, and cable. Our findings demonstrate that users tend to focus on tangible, personal-use aspects of sustainability, such as packaging and waste reduction, while overlooking more technical concerns like manufacturing processes. We also demonstrate the ability to generate design leads tailored to specific product features, such as printer toner or earring material properties. As the volume of user feedback grows, this research highlights the need for efficient methods to identify trends, uncover redesign opportunities for enhanced sustainability, and improve how sustainability is communicated through product features and user experiences, creating a valuable resource for future research.